A gear reducer, also called a gearbox, connects a motor mechanically to a driven load. Gear reducers enable the change of torque and speed of a system with respect to the load. A collection of gears make up a reduction gear assembly. Read More…
We offer premium speed reducers and motion control components. These deluxe parts are designed for a wide range of purposes and our engineers are willing to assist you with determining the best speed reducer.
At Nordex, we are dedicated to delivering precision-engineered speed reducers and power transmission solutions that drive efficiency, reliability, and innovation across industries. With decades of expertise, we design and manufacture speed reducers that meet the highest standards of performance, enabling seamless integration into machinery and equipment that demand consistent output and long-term ...

At Winsmith, we take pride in being a trusted leader in the design and manufacturing of high-performance speed reducers that meet the evolving needs of industries worldwide. With decades of experience, we have refined our engineering expertise to deliver precision-driven power transmission solutions that enhance efficiency and reliability in even the most demanding environments.

At Matex Products, we pride ourselves on being a trusted name in motion control solutions, with a strong focus on precision-engineered speed reducers. For decades, we have been dedicated to designing and manufacturing high-quality components that help businesses across industries achieve smoother, more reliable performance in their machinery and automation systems.

More Gear Reducer Manufacturers

How Gear Reducers Work
Gear reducers, also known as speed reducers or gearboxes, are essential mechanical devices used in a wide variety of industrial and commercial applications. They serve to decrease rotational speed and increase torque output by using a system of gears with varying ratios. This process is crucial for optimizing performance, energy efficiency, and lifespan of countless types of equipment, including conveyor systems, manufacturing machinery, robotics, automotive drivetrains, and more.
Most high-efficiency machinery operates at high speeds, but often, the application requires a lower, controlled speed with a corresponding increase in torque. A gear reducer provides this solution by coupling a large gear to a smaller gear, causing an energy shift. In this arrangement, the smaller (driven) gear rotates multiple times for every rotation of the larger (driver) gear, effectively reducing speed and boosting torque output.
Gear reduction occurs at specific gear ratios—such as 2:1, 5:1, or higher—depending on the needs of the end application. By altering the ratio between the driver and driven gears, gear reducers can precisely control output speed and torque, enabling optimized performance for electric motors, engines, or other power sources. This makes gear reducers a foundational component in mechanical power transmission systems.
Looking for more detail? What are the main benefits of using a gear reducer in your application? Explore the sections below for a deeper understanding of use cases, energy savings, and equipment protection advantages.
Types of Gear Reducers
There are several types of gear reducers, each designed for specific applications, load requirements, and space constraints. Understanding the unique features and benefits of each type can help you select the most appropriate gearbox for your project or industrial machinery.
Planetary Gear Reducer
Planetary gear reducers are a premium choice in applications demanding high torque density, compact size, and superior reliability. These reducers feature a central sun gear, orbiting planet gears, and an outer ring gear, all working together to evenly distribute load and minimize stress on individual components. The planet gears are supported by the output shaft and rotate in lockstep with the inner gear ring, delivering smooth power transmission.
Key advantages of planetary gearboxes include high efficiency (often above 95%), long operational life, and the ability to handle large shock loads. Their compact design makes them ideal for robotics, servo drives, automation systems, and aerospace equipment where both space and precision are critical. Power splitting and multiple teeth meshing provide quiet operation and minimal backlash, further enhancing their suitability for demanding industrial environments.

Common uses: Robotics, packaging machinery, conveyor systems, servo drives, and any setting where high torque and precision are required.
Buyer tip: Looking for a high-precision solution? Compare planetary gear reducer manufacturers for custom configurations and expert technical support.
Helical Gear Reducer
Helical gear reducers are widely used for their smooth operation, high load capacity, and energy efficiency. Unlike spur gears, helical gears have slanted tooth traces, which increase the gear mesh contact ratio and enable quieter, more durable operation. This design also allows for higher torque transfer and increased surface area contact, making helical gearboxes ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Their synchromesh tooth profile ensures a consistent transfer of power with minimal vibration and noise, even at high speeds. Helical gear reducers are often favored in material handling equipment, elevators, mixers, and extruders due to their robustness and durability under continuous operation.
Typical industries: Manufacturing, mining, food processing, chemical plants, and material handling systems.
Considering a helical gear reducer? How does a helical gear reducer compare to other gearbox types in terms of efficiency and noise? Contact our experts for detailed technical advice tailored to your application.
Magnetic Gear Reducers
Magnetic gear reducers utilize the principles of magnetic attraction and repulsion to transmit torque without physical contact between moving parts. By employing permanent magnets or electromagnets in place of traditional gear teeth, these reducers eliminate mechanical wear, thus extending service life and reducing maintenance requirements.
Because there is no direct contact, magnetic gearboxes operate with virtually zero backlash and are immune to lubrication-related failures. This makes them an excellent choice in environments where contamination control and reliability are paramount, such as cleanrooms, food and beverage processing, and medical devices.
Advantages include:
- No need for lubrication or sealed housings
- Silent operation and minimal vibration
- Intrinsic overload protection—magnetic slip prevents mechanical damage
- Long-term reliability and reduced total cost of ownership
Want to know if magnetic gear reducers are right for your process? What are the maintenance advantages of magnetic gearboxes compared to conventional gear reducers? Explore our in-depth guides or contact a specialist today.
Spur Gear Reducers
Spur gear reducers are the simplest and most cost-effective type of gearbox, featuring straight teeth that are parallel to the gear axis. Known for their high efficiency (often exceeding 98%) and straightforward design, spur gearboxes are widely used in applications where noise and vibration are less of a concern, but reliability and simplicity are valued.
Multiple gears can be combined within a spur gearbox to deliver a range of gear ratios, making them highly versatile for both industrial and consumer products. Their minimal backlash and strong durability ensure stable, consistent performance in a wide range of mechanical systems.
Common applications: Printing presses, conveyors, machine tools, and basic industrial automation systems.
Need a straightforward, budget-friendly solution? How do spur gear reducers compare with helical or planetary reducers for your specific needs? Access our comparison tools or speak with an adviser.
Bevel Gear Reducers
Bevel gear reducers are engineered for applications requiring a change in the direction of shaft rotation, typically by 90 degrees. These reducers utilize bevel gears with conical profiles, allowing power transmission between intersecting shafts. Angular bell crank designs enable adjustments from transverse to longitudinal motion, making bevel gearboxes particularly useful in compact layouts or complex machinery.
With the ability to integrate three-phase asynchronous motors, synchronous motors, and servo motors, bevel gear reducers deliver powerful, quiet, and energy-efficient performance. They are commonly used in automotive differentials, mining equipment, and heavy machinery where space efficiency and directional flexibility are priorities.

Use cases: Conveyor belts, right-angle drives, agricultural machinery, and power transmission systems in vehicles.
Trying to fit a gearbox into a tight space? What types of motors are compatible with bevel gear reducers? Find compatible solutions by browsing our product catalog.
Worm Gear Reducers
Worm gear reducers consist of a worm (a screw-like input shaft) meshing with a worm gear (a toothed output wheel) at a right angle. Worm gearboxes are renowned for their ability to achieve very high reduction ratios in a compact, space-saving package. This makes them ideal for applications where a significant decrease in speed and a substantial increase in torque are required.
Worm gear reducers provide self-locking capabilities, preventing back-driving and enhancing safety in lifting or hoisting applications. They are also appreciated for their smooth, quiet operation and shock absorption characteristics. However, they typically have lower efficiency than helical or planetary gearboxes due to sliding contact between the worm and gear teeth.
Popular applications: Material lifts, conveyors, gates, hoists, and compact machinery where safety and space constraints are paramount.
Interested in maximizing torque in a small footprint? What are the advantages and limitations of worm gear reducers for your equipment? Dive deeper into our worm gearbox resource center.
Hypoid Gear Reducers
Hypoid gear reducers are a specialized form of bevel gearbox, featuring off-axis, spiral-shaped gears that enable smooth, quiet, and efficient power transmission between non-intersecting shafts. The unique offset in the gear geometry allows hypoid gears to transmit higher loads with reduced noise and vibration compared to straight bevel gears or worm gearboxes.
Hypoid gear reducers are especially valued in automotive drivetrains, heavy machinery, and industrial automation where high torque, compact design, and quiet operation are required. They deliver exceptional durability, low heat generation, and allow for flexible mounting orientations, making them a versatile choice for engineers and machine designers.
Sample applications: Automotive axles, large conveyors, printing presses, and high-torque robotics.
Need a smooth, high-load solution for your machinery? How do hypoid gear reducers outperform worm or bevel gearboxes in your industry? Connect with a technical consultant for a side-by-side analysis.
Key Benefits and Use Cases for Gear Reducers
Gear reducers are pivotal for a wide range of industries, providing essential benefits for system performance, reliability, and operational cost savings. Whether you’re integrating a gearbox into new machinery or retrofitting an existing system, understanding the benefits can help inform your selection process:
- Increased torque output: Reduces the load on motors and enables smaller, more efficient motor selection.
- Controlled speed: Offers precise control over output speed for process optimization.
- Energy efficiency: Minimizes wasted energy by aligning power delivery with operational requirements.
- Enhanced equipment lifespan: Reduces mechanical stress and wear on motors and driven equipment.
- Space savings: Compact gearboxes allow for flexible machine layouts and integration in tight spaces.
- Noise and vibration reduction: Advanced gear designs, such as helical and hypoid, minimize operational noise.
- Safety features: Self-locking and overload protection in specific gearbox types improve operator and equipment safety.
- Low maintenance options: Magnetic and sealed gearboxes eliminate lubrication requirements and reduce downtime.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Gear reducers are found across diverse sectors, each with unique performance requirements and challenges. Here are some common industry applications:
- Manufacturing: Conveyor belts, assembly lines, CNC machines, and automated material handling systems rely on gear reducers for precision and power efficiency.
- Automotive: Used in drivetrains, differential systems, and electric vehicle powertrains for controlled torque delivery and improved fuel efficiency.
- Robotics: Precision gearboxes like planetary reducers enable accurate movement and positioning in robotic arms and automation.
- Mining and heavy industry: Helical, bevel, and worm gearboxes provide the strength and durability needed for crushers, mills, and heavy conveyors.
- Renewable energy: Gear reducers in wind turbines and solar tracking systems convert high-speed rotation to usable torque for power generation.
- Food and beverage: Magnetic and sealed reducers are chosen for hygienic, contamination-free environments.
- Medical equipment: Compact, precise gearboxes are used in imaging systems, surgical robots, and patient handling devices.
- Aerospace: Planetary and hypoid gearboxes are critical for actuators, control systems, and propulsion components.
Curious about the optimal gearbox for your industry? Which gear reducer type offers the best balance of efficiency, size, and cost for your application? Start your search with our interactive comparison tool or reach out for a tailored solution.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Gear Reducer
The process of choosing the right gear reducer involves balancing technical requirements, operational needs, and budget constraints. Consider the following key decision factors:
- Required torque and speed: Calculate the output torque and speed needs based on your application’s load and duty cycle.
- Efficiency: Prioritize gear reducer types that deliver optimal energy transfer with minimal losses for your use case.
- Size and footprint: Evaluate available space and mounting options, especially in retrofits or compact systems.
- Noise and vibration: Choose advanced gear designs for environments sensitive to sound and movement.
- Maintenance and serviceability: Assess lubrication needs, accessibility, and long-term maintenance costs.
- Budget: Align product selection with available capital and operational expense expectations.
- Environment: Account for exposure to dust, moisture, chemicals, and temperature extremes.
- Backlash and precision: Critical for robotics, automation, and applications requiring accurate motion control.
- Lifespan and reliability: Factor in product reputation, warranty, and track record in similar environments.
Not sure where to start? How do you calculate the optimal gear ratio for your machinery? Use our free gear ratio calculator or consult with an application engineer.
Choosing the Correct Gear Reducer Manufacturer
To ensure the best outcome when purchasing gear reducers, it’s essential to partner with a reputable gear reducer manufacturer. Here are the steps you should follow to make an informed decision:
- Research and compare at least four to five gear reducer manufacturers using our comprehensive manufacturer directory.
- Review each manufacturer’s business profile, which details their areas of expertise, production capabilities, and industry certifications.
- Visit manufacturer websites using our proprietary website previewer to assess product range, technical documentation, and support resources.
- Use our streamlined RFQ (Request for Quote) form to contact multiple gear reducer companies and obtain competitive quotations for your specific requirements.
- Directly communicate with manufacturers via their contact forms to clarify technical details, customization options, lead times, and after-sales support.
Choosing the right supplier can influence not just the cost and quality of your gear reducer, but also long-term performance, maintenance resources, and total cost of ownership.
Ready to take the next step? Contact leading gear reducer manufacturers now or request a personalized quote to get started on your project.
Frequently Asked Questions: Gear Reducers
- What is the difference between a gearbox and a gear reducer? While often used interchangeably, a gear reducer specifically refers to a device that reduces input speed and increases torque, whereas a gearbox can include both reducing and increasing gear arrangements.
- Can gear reducers be customized for unique applications? Yes, most manufacturers offer custom gear reducers with specific gear ratios, mounting options, and material choices to suit specialized applications and environmental conditions.
- How do I maintain my gear reducer for optimal performance? Regular inspection, proper lubrication (for mechanical gearboxes), and adherence to manufacturer maintenance schedules will maximize lifespan and efficiency. Magnetic gear reducers require minimal maintenance.
- What is backlash, and why is it important? Backlash is the slight movement between gear teeth when direction is reversed. Low-backlash gear reducers are crucial for precision applications such as robotics and CNC machinery.
- How can I increase energy efficiency with gear reducers? Choose high-efficiency gear types (such as planetary or helical), ensure proper sizing, and maintain equipment according to recommendations to minimize energy losses.
Still have questions? What technical specifications are most critical when selecting a gear reducer? Explore our technical resources or schedule a consultation with our engineering team for tailored support.
Get Started: Find the Best Gear Reducer for Your Needs
Whether you’re modernizing an existing system or designing new equipment, gear reducers play a critical role in optimizing performance and reliability. By understanding the different types of gearboxes, their unique features, and how to match them to your application, you can ensure years of trouble-free operation and maximize your return on investment.
Explore our directory to compare leading gear reducer manufacturers, review technical specifications, and get expert advice. Ready to make a decision? Contact suppliers for a quote or dive into our knowledge base for more in-depth guides and resources.







 Ball Bearings
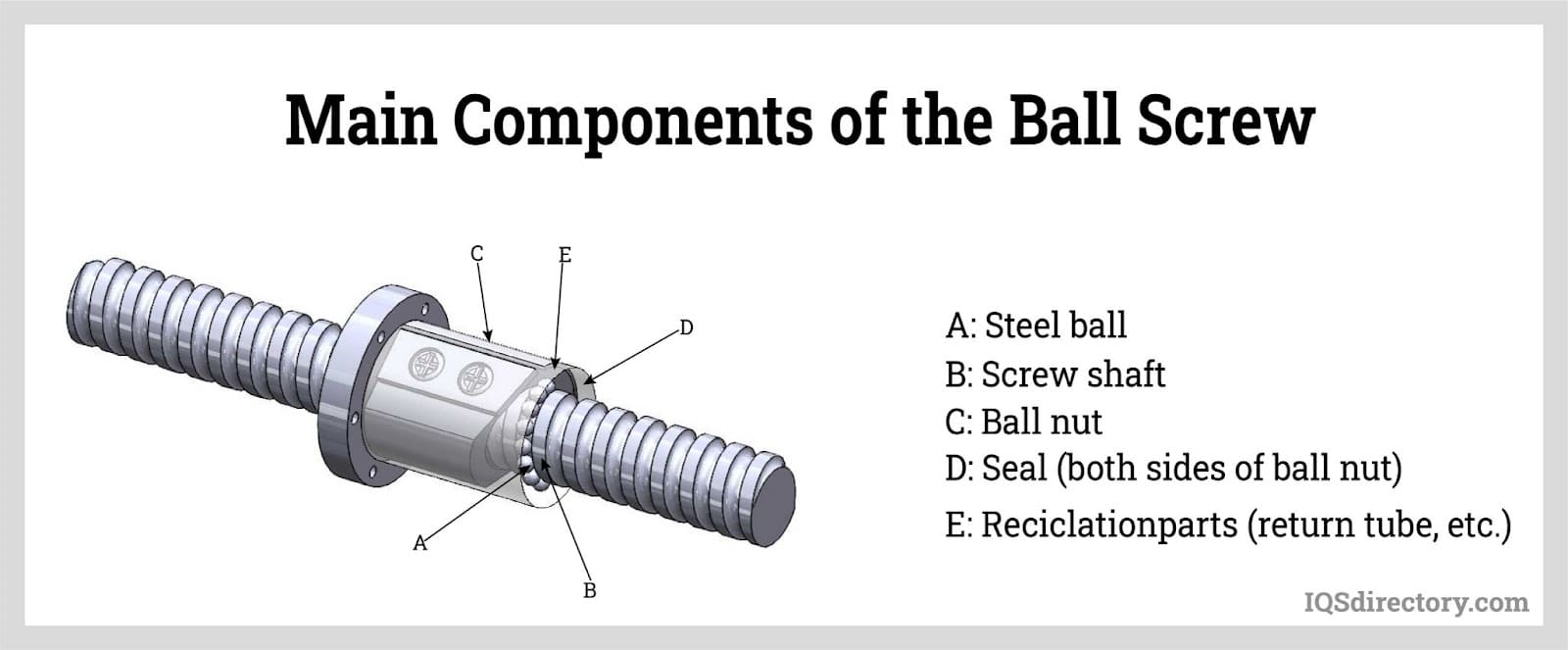
Ball Bearings Ball Screws
Ball Screws Electric Motors
Electric Motors Friction Materials
Friction Materials Gears
Gears Quick Release Couplings
Quick Release Couplings Shaft Couplings
Shaft Couplings Speed Reducers
Speed Reducers Timing Belting
Timing Belting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services